Support Articles
Find Command Help Using the Terminal
Even experienced Linux users frequently utilize knowledge resources to find proper syntax for Terminal commands, or to discover options for known commands. All Linux shells support common utilities that search for and explain commands for a given task. These commands may navigate the user to a text file or navigable structure of help files, while others simply print output into the current Terminal session.
Why Find Help Using the Terminal?
Issues may disable user access to the desktop environment, including the web browser. In these scenarios, users can still find help that displays as output in a Terminal session. Users who still have access to a browser or second computer can find help using the Ubuntu or Debian manpage websites. The commands below are entered in a Terminal session. In Pop!_OS, Terminal sessions can be started by pressing Super + t.
--help
--help prints out a shortened version of the man page, usually including a brief example and all options for a command. --help prints output to the terminal session without navigating away from the shell prompt.
Use case: A user wants to quickly reference all options for a known command in the current Terminal session.
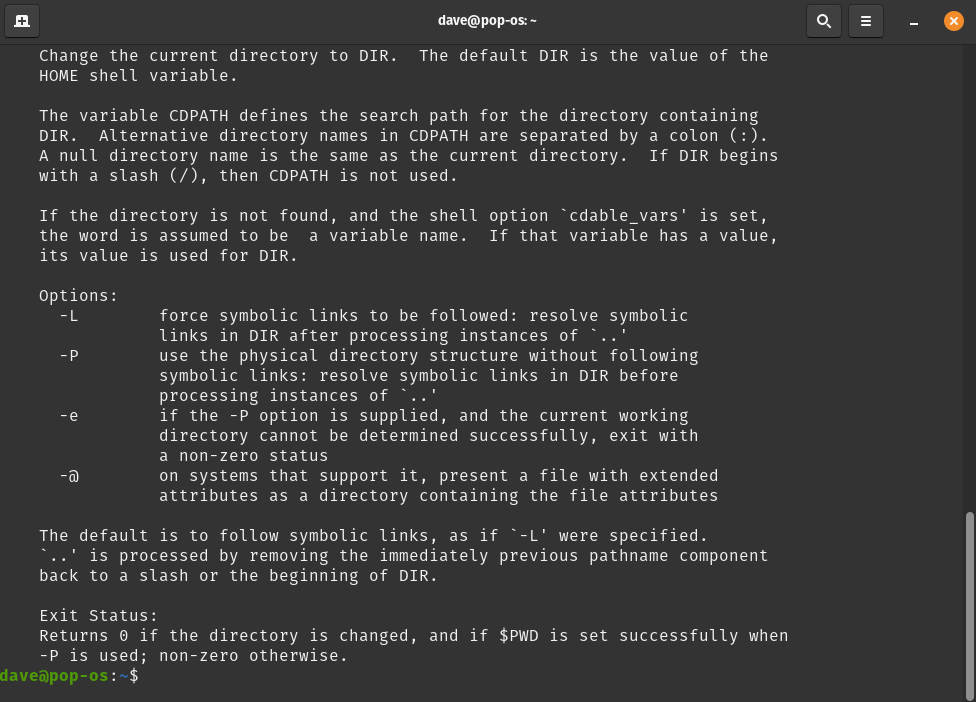
Usage: Type a command + --help, then hit Enter. This example uses the cd command. Commands must be an exact match.
cd --help
whatis
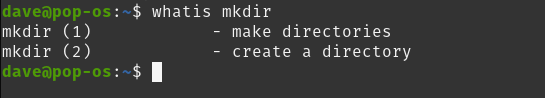
whatis provides a very short description of a command's functionality.
Use case: A user wants a very brief reminder of a known command's functionality printed in the current Terminal session.
Usage: Type whatis + command, then hit Enter. This example uses the mkdir command. Commands must be an exact match.
whatis mkdir
dpkg -S
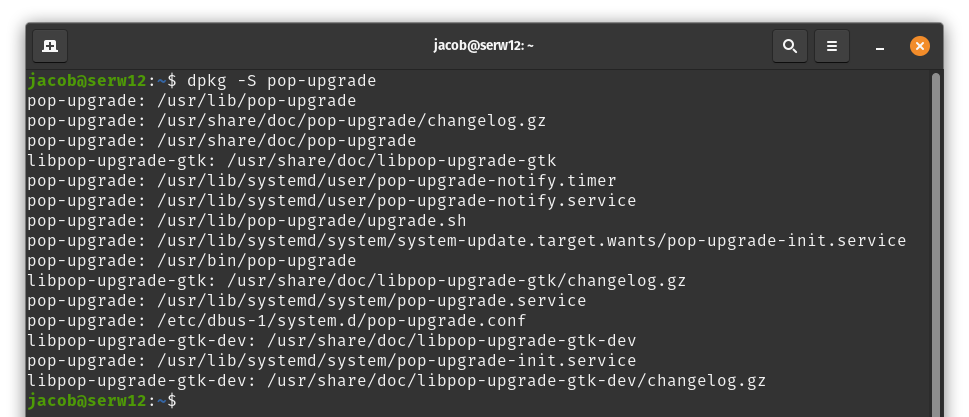
dpkg -S provides an index of files installed from a package.
Use case: A user is attempting to learn about commands included with a recently installed package.
Usage: Type dpkg -S + package name, then hit Enter. This command only works with currently-installed packages.
dpkg -S pop-upgrade
which & dpkg -S
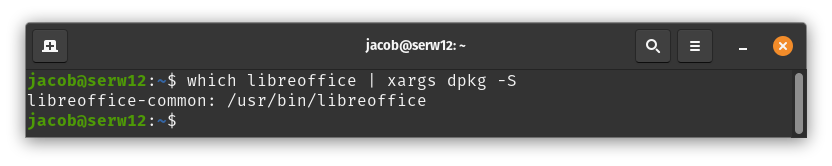
which provides the file location of a command. The output of which can be passed into dpkg -S to perform a search of associated packages.
Use case: A user would like to know which installed package provides a specific command.
Usage: Type which + command, then pipe the output of which into dpkg -S using xargs. The xargs command allows users to pass the output of a command as standard input into another command. The below example searches for the path of the libreoffice command, and then searches for the package associated with that path.
which libreoffice | xargs dpkg -S
Commands within symlinked directories
Users may see an error stating no matching path can be found:
which mkdir | xargs dpkg -S
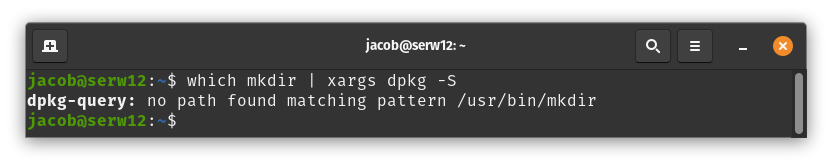
This occurs when a package is programmed to install a file to one directory, but that directory is symlinked to another directory on the system; in this situation, the package manager installs the file to a directory that differs from the original package's progamming. The following directories are commonly symlinked on Pop!_OS systems:
| Symlink Name | Actual Directory |
|---|---|
| /bin | /usr/bin |
| /sbin | /usr/sbin |
| /lib | /usr/lib |
| /lib64 | /usr/lib64 |
If dpkg -S is unable to find a match, run which manually, remove /usr from the beginning of the output, and reattempt the command:
which mkdir
dpkg -S /bin/mkdir
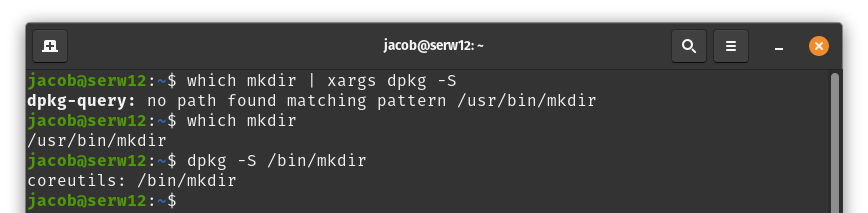
In the above example, the mkdir command (which comes from the coreutils package) was supposed to be installed to /bin/mkdir, but is located at /usr/bin/mkdir instead because /bin is a symlink to /usr/bin in Pop!_OS.
Commands symlinked to other files
Sometimes, a command may not be an executable itself, but may be symlinked to an executable installed by a different package. To check if this is the case, after getting the command's path with which, run the path through ls -l to display any link information:
which reboot
ls -l /usr/sbin/reboot
dpkg -S /bin/systemctl
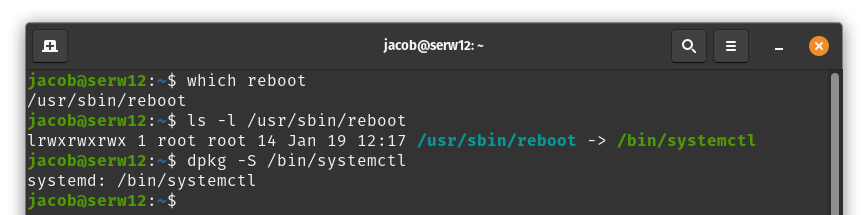
In the above example, the reboot command is located at /usr/sbin/reboot (which is installed from the systemd-sysv package), but that file is actually a symlink to /bin/systemctl (which comes from the systemd package.)
apropos
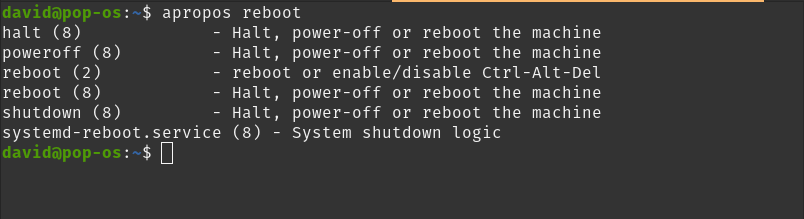
apropos performs a keyword search on command man pages. This is useful when searching for a command by its function. apropos prints output to the terminal session without navigating away from the shell prompt.
Use case: A user can't remember the specific name of a command, but knows keywords commonly used to describe the command's functions.
Usage: Type apropos + keyword, then hit Enter. This example searches for commands related to the reboot keyword.
apropos reboot
man
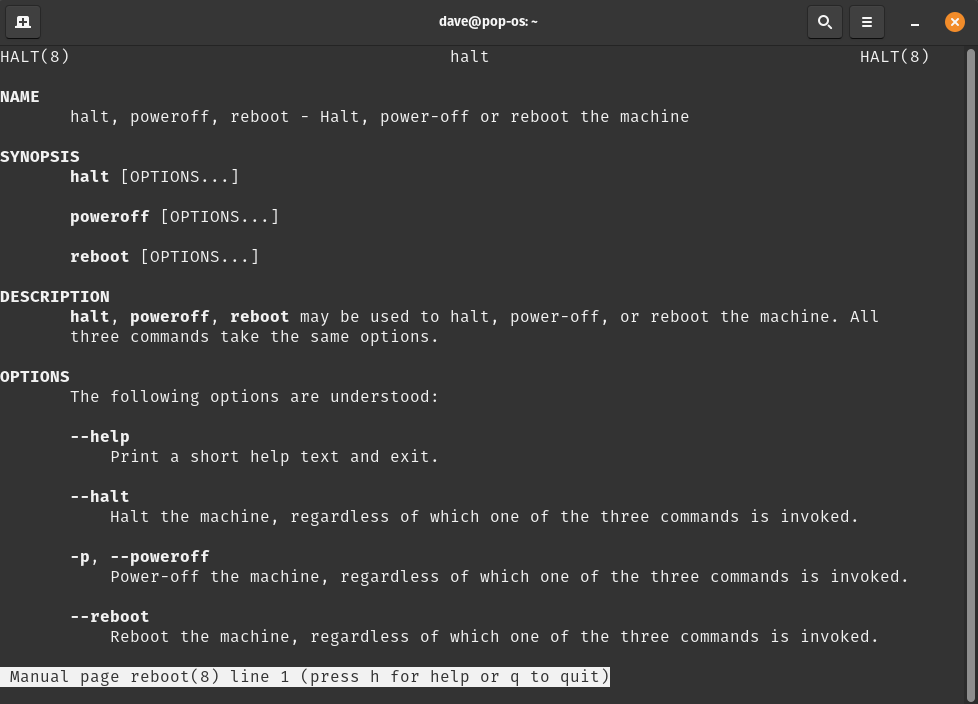
man is short for manual pages. A command's manual page is a consistently structured text file describing the command's function, usage syntax, options, and similar commands. man opens a manpage in the terminal session, and pressing q exits the manpage and returns the user to the shell prompt.
Use case: A user wants to see actions performed by a specific command, and available options to modify the outcome of the command.
Usage: Type man + any command into a Terminal session, then hit Enter. This example uses the reboot command.
man reboot
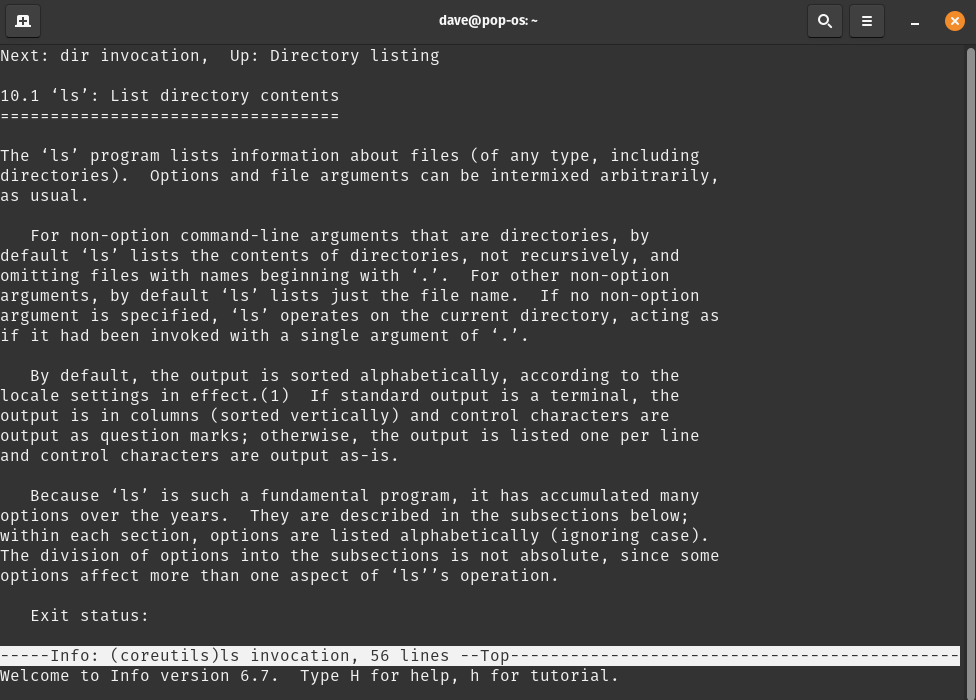
info
info pages are similar to man pages; however, their descriptions for command usage are more in-depth and include examples of output. Users can also navigate to other related info pages using hypertext links within the info page. info opens an info page in the Terminal session, and pressing q exits the manpage and returns the user to the shell prompt.
| Key | Function |
|---|---|
| Arrow Up | Move up one line |
| Arrow Down | Move down one line |
| Tab | Move to next hyperlink |
| Enter | Select a hyperlink |
| Page Up | Move up one page |
| Page Down or Space bar | Move down one page |
| n | Move to next info page |
| p | Move to previous info page |
| q | Exit the info page |
Use case: A user wants to see examples of command usage, command output, and easily navigate to commands offering related or supporting functionality.
Usage: Type info + any command into a Terminal session, then hit Enter. This example uses the ls command.
info ls